Definition of greenhouse gas any of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect Water vapor is an important gas for the study of climate and weather because of its role as a natural greenhouse gas as well as its relationship to clouds and precipitationCommon examples of greenhouse gases, listed in order of abundance, include water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, and any fluorocarbons Although water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas, it is a relatively ineffective one Greenhouse gas, any gas capable of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor are the most important greenhouse gases
Economic Approaches To Greenhouse Warming
What is an example of a greenhouse gas
What is an example of a greenhouse gas-The greenhouse effect is the term scientists use to describe the way that greenhouse gases trap the sun's energy As the sun's rays enter Earth's atmosphere, they passGreenhouse definition is a structure enclosed (as by glass) and used for the cultivation or protection of tender plants How to use greenhouse in a sentence




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Definition Impact Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
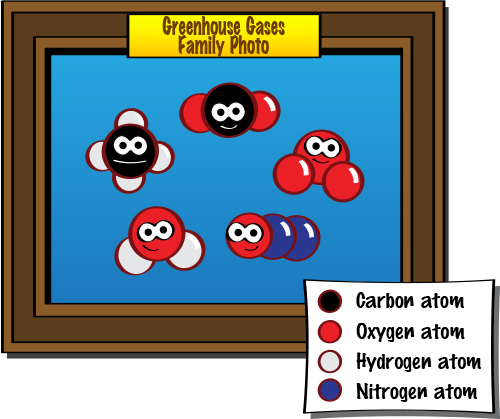
Greenhouse Gases Examples The Primary GHGs are Water vapor Carbon dioxide Methane Nitrous oxide Ozone Other GHGs are carbon monoxide, fluorinated gases, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), black carbon (soot), and brown carbon Among the greenhouse gases, only water vapor can absorb both incoming (UV) and outgoing (infrared) radiationWhen we talk about greenhouse gases, we're referring to carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons and sulphur hexafluoride Join us on social! Greenhouse Earth Overview A "greenhouse Earth" is a period during which no continental glaciers exist anywhere on the planet Additionally, the levels of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases (such as water vapor and methane) are high, and sea surface temperatures (SSTs) range from 28 °C (4 °F) in the tropics to 0 °C (32 °F) in the polar regions
Greenhouse gas definition Greenhouse gases are the gases which are responsible for causing the greenhouse effect Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examplesCarbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide are important greenhouse gases Global warming In addition to greenhouse gases (eg carbon dioxide, methane, ozone) in the atmosphere increases the temperature of the earth These gases remain the lowest part of the earth's atmosphere and do not allow solar radiation to reflect back into spaceLearn the definition of 'greenhouse gasesrelated radiative forcing' Check out the pronunciation, synonyms and grammar Browse the use examples 'greenhouse gasesrelated radiative forcing' in the great English corpus
Learn the definition of 'sink of greenhouse gases' Check out the pronunciation, synonyms and grammar Browse the use examples 'sink of greenhouse gases' in the great English corpus Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases are Water vapor;Climate Change Definition vs Global Warming Definition According to the US Geological Survey, global warming is just one aspect of climate change In fact, they say that global warming refers to the rise in global temperatures due mainly to the increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere




Greenhouse Effect What Is It Definition And Role In Global Warming



Economic Approaches To Greenhouse Warming
Greenhouse gases are a hot topic (pun intended) when it comes to global warming These gases absorb heat energy emitted from Earth's surface and reradiate it back to the ground In this way, they contribute to the greenhouse effect, which keeps the planet from losing all of its heat from the surface at nightGreenhouse gases (GHG) are gaseous compounds that can emit ultraviolet radiation within a certain thermal infrared range 76 Greenhouse gases retain high temperatures in the lower atmosphere, thus allowing less heat to escape back to space This subsequently results in the greenhouse effect and global warmingGreenhouse gases are certain gases in the atmosphere (water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane, for example) that trap energy from the sun Without these gases, heat would escape back into space and Earth's average temperature would be about 60º F colder



Q Tbn And9gcs3 Vn3xnwnq9ifctpyrsa2ofh2ymxfw2rxlcy7frr77uflqr Usqp Cau




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Definition Impact Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
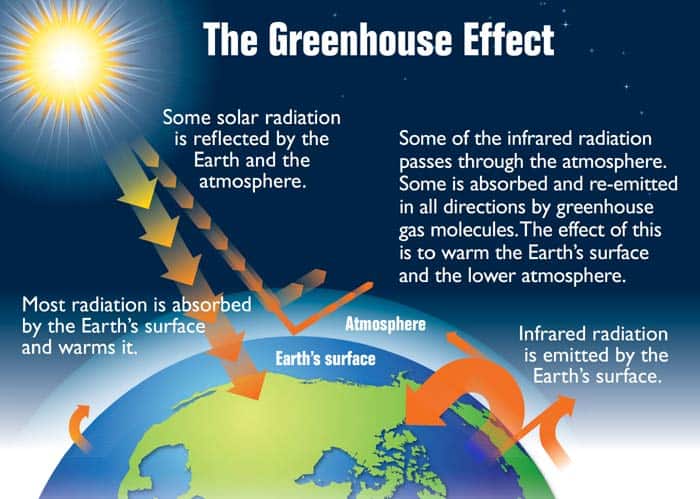
A greenhouse gas is a gas which reflects radiation that the Earth emits, and stops it from being lost into space This makes the Earth hotter than it would be without greenhouse gases This is called the " greenhouse effect " Most greenhouse gases are natural water vapor is the most common, and causes most of the greenhouse effect on EarthGreenhouse Effect Example Bright sunlight will effectively warm your car on a cold, clear day by the greenhouse effectThe longer infrared wavelengths radiated by sunwarmed objects do not pass readily through the glass The entrapment of this energy warms the interior of the vehicleLearn more about climate change and discover ways to take action




Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
A carbon footprint corresponds to the whole amount of greenhouse gases (GHG) produced to, directly and indirectly, support a person's lifestyle and activities Carbon footprints are usually measured in equivalent tons of CO2, during the period of a year, and they can be associated with an individual, an organization, a product or an event, among others In general, greenhouse gases constitute just almost 1% of the total gases present in the atmosphere Their concentrations are dependent on the balance between the "sources" and "sinks" that function to create and destroy these gases respectivelyAnthropogenic activities tend to increase these concentrations by either introducing new types of gases in the air or'It is virtually certain that increasing atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases will cause global surface climate to be warmer' More example sentences 'Although an excess of greenhouse gas results in global warming, naturally occurring greenhouse gases are beneficial in keeping our planet at a comfortable temperature'




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change
Agricultural Practices That sequester Carbon or Reduce the Emissions of other Greenhouse Gases KEY AGRICULTURAL PRACTICES TYPICAL DEFINITION AND SOME ExAMPLES EFFECT ON GREENHOuSE GASES Conservation or riparian buffers Grasses or trees planted along streams and croplands to prevent soil erosion and nutrient runoff into waterways The greenhouse effect is the process by which the Earth's atmosphere retains heat due to the accumulation of greenhouse gases such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane in the air In contrast, global warming is the average increase in the temperature of the Earth caused due to the greenhouse effectProvided, however, that the definition of the term "Greenhouse Gas", as set forth in the immediately preceding sentence, shall be deemed revised to include any update or other change to such term



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Lesson For Kids Study Com
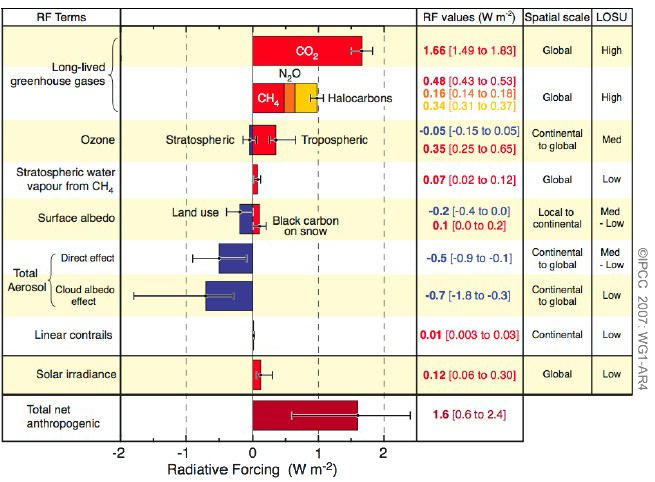
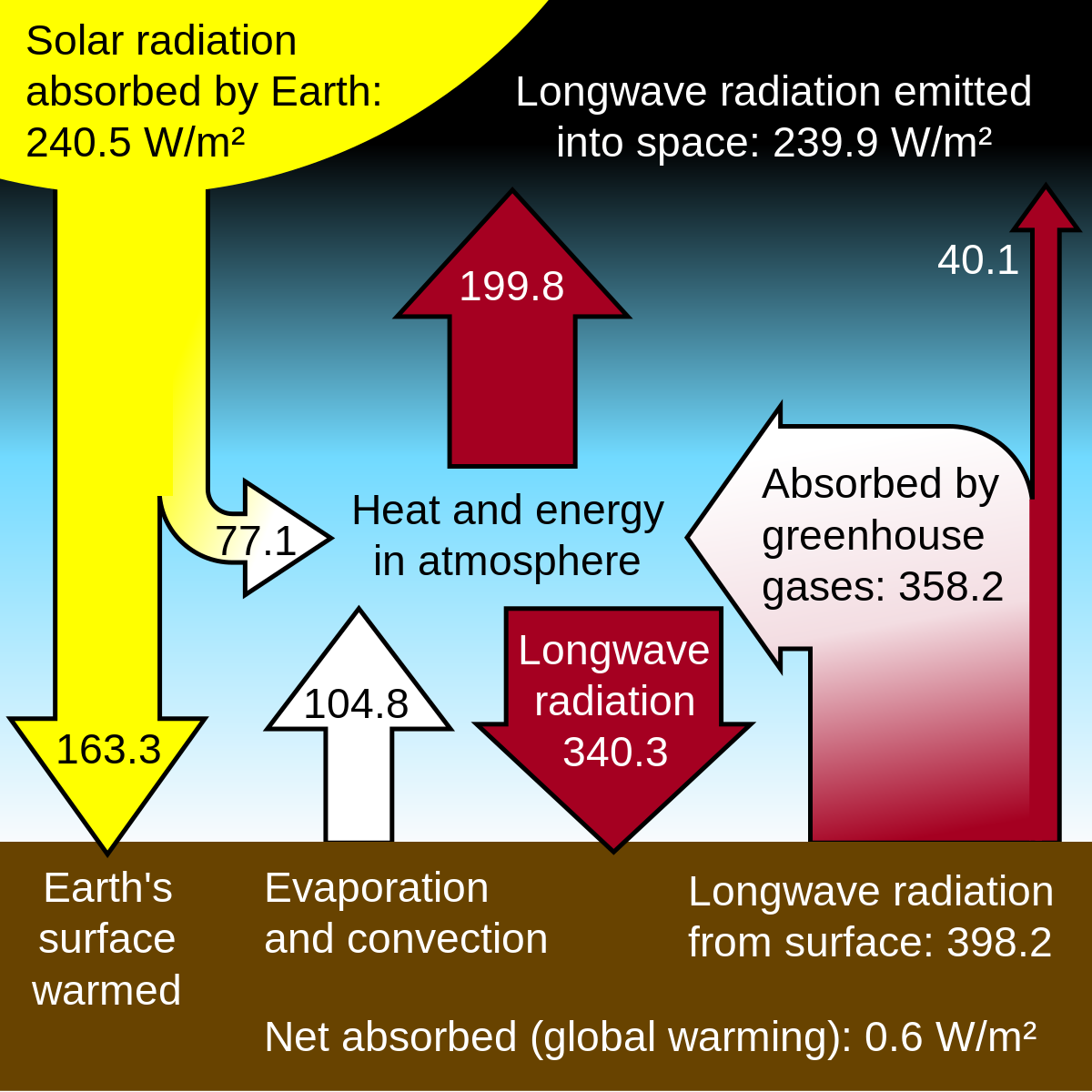
Greenhouse effect and global warming I t is only trace gases in the at mosphere (Table 1) such as CO 2 (004%), CH 4 (%), O 3 (3 × 10 − 6 %) and chloroflu orocarbons such as CF 2 Cl 2 (5 A greenhouse gas is a gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation in the atmosphere Carbon dioxide is considered to be a greenhouse gas because it traps heat radiated into the atmosphere Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space This keeps the Earth warmer than it would be without these gases Greenhouse gases are not a bad thing in




Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students




Boundary Definition And Examples Of Energy Related Ghg Emissions Download Table
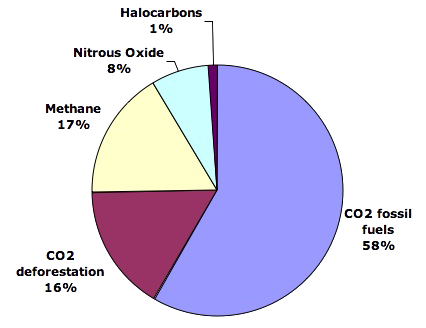
In general, fluorinated gases are the most potent and longest lasting type of greenhouse gases emitted by human activities There are four main categories of fluorinated gases—hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6 ), and nitrogen trifluoride (NF 3 )Morris A (Bud) Ward Water vapor and what expert scientists consider the four other 'most important' greenhouse gases comprise the veritable 'hit parade' of greenhouse gases that trap heat in Earth's atmosphere and contribute to overall warming across the globe There's a whole family of greenhouse gases (GHGs) Greenhouse Gas (GHG) The gases that have the property of absorbing infrared radiations from the Earth's surface and radiating it back to the Earth's surface, leading to a Greenhouse phenomenon, are known as Greenhouse gases Methane, Carbon Dioxide and Water Vapour are some of the leading examples of Greenhouse gases




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Measuring Urban Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Challenge Of Comparability
Greenhouse Gases at EPA Before there were federal requirements to do so, EPA had developed a greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions inventory and established reduction targets to decrease its GHG footprint There are three types of GHG emissions EPA tracks and works to reduce Scope 1 GHG emissions are direct emissions from sources that are owned or Examples of gases at standard temperature and pressure include air (a mixture of gases) chlorine at room temperature and pressure ozone oxygen hydrogen water vapor orGreenhouse gas (GHG) Description Greenhouse gases are those gaseous constituents of the atmosphere, both natural and anthropogenic, that absorb and emit radiation at specific wavelengths within the spectrum of terrestrial radiation emitted by




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay




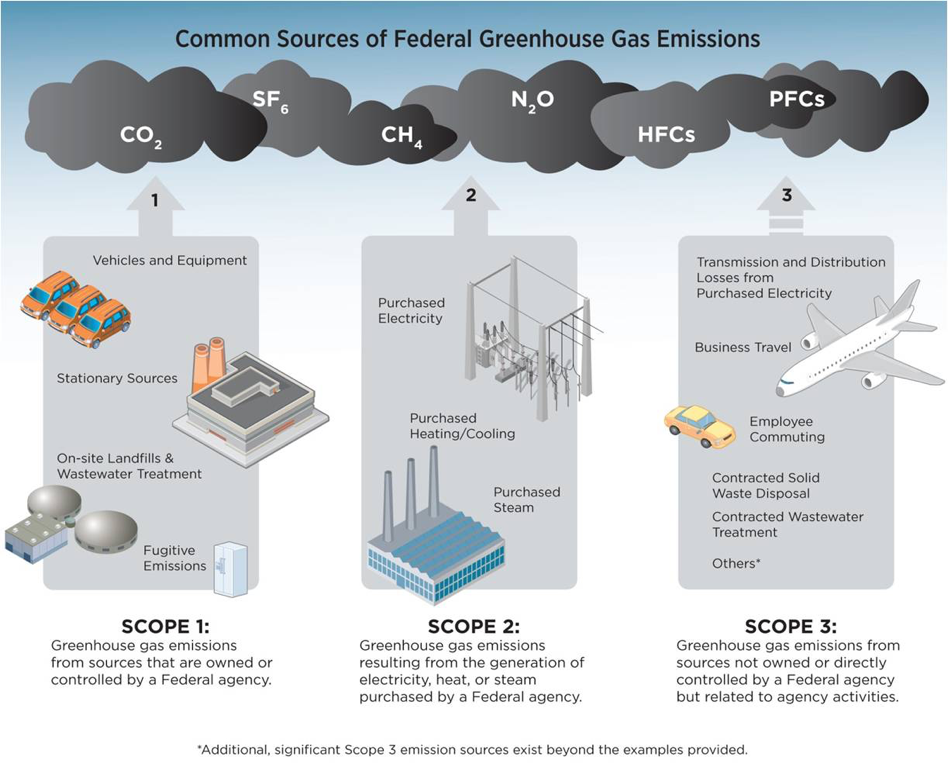
Scope 1 2 And 3 Emissions Overview To Direct And Indirect Emissions Ecochain
Greenhouse gases are those gases in the atmosphere that have an influence on the earth's energy balance They cause the socalled greenhouse effect The best known greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane and nitrous oxide, can be found naturally inGreenhouse gases means the aggregate group of six greenhouse gases carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, and sulfur hexafluorideLearn the definition of 'indirect greenhouse gases' Check out the pronunciation, synonyms and grammar Browse the use examples 'indirect greenhouse gases' in the great English corpus




What Is Climate Change Definition And Examples Market Business News




Sources And Sinks American Chemical Society
5 major greenhouse gases and their sources 1 Carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide has the chemical formula CO2 It is a very harmful and damaging greenhouse gas This gas is released into our atmosphere largely through the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gasGreenhouse gas definition, any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and the fluorocarbons See more DICTIONARYCOMGreenhouse gases may be defined or expressed in terms of a metric ton of CO2equivalent, in order to allow comparison between the different effects of gases on the environment;



Greenhouse Effect Keeping The Balance Nasa Climate Kids




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change
A greenhouse gas is simply any atmospheric gas that traps heat within the atmosphere These gases allow sunlight to pass through the atmosphere




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




What Is Greenhouse Gas Definition Causes Effects Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia



Climate Change Project Ll Part 2 स ट र ब र ड द व र d47




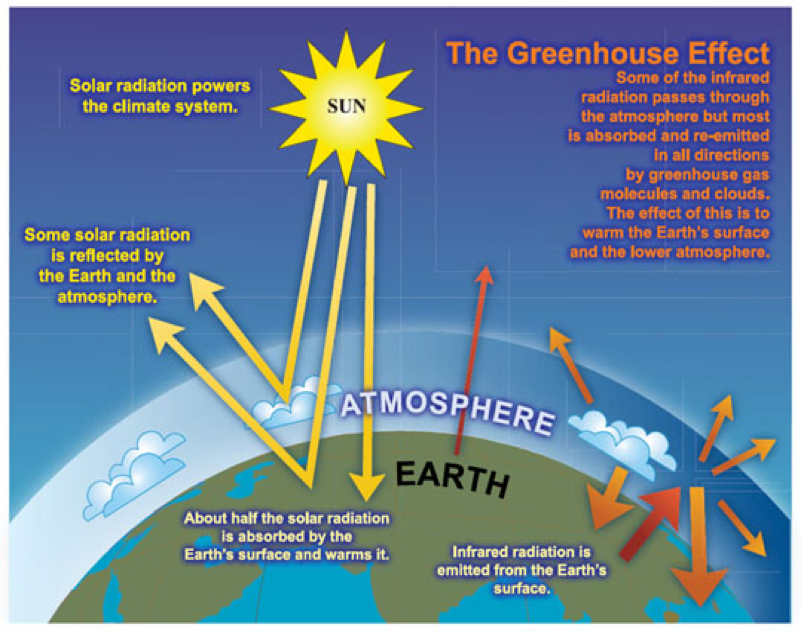
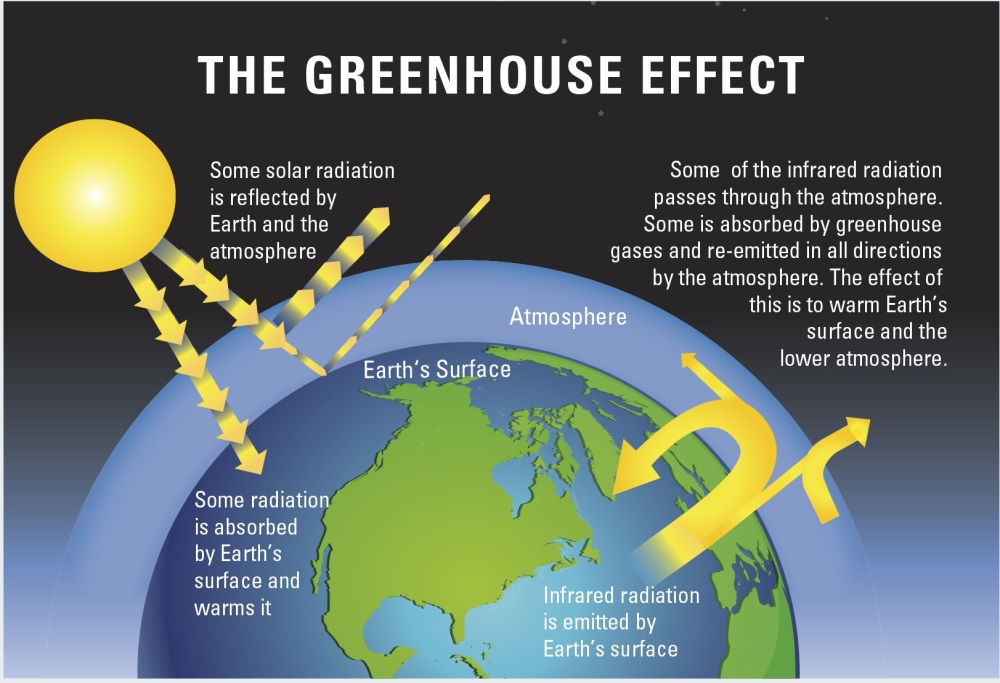
The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Measuring Urban Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Challenge Of Comparability




Properties Of Greenhouse Gases



Greenhouse Gas Reduction




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Revised Papers Due April 17 N Strunk And




Greenhouse Gas Ghg Meaning And Several Examples




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



Environment For Kids Global Warming




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Gases Or Gasses




What Are Greenhouse Gases Lesson For Kids Study Com




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects



Where Carbon Is Released From The Ocean Into The Atm



Greenhouse Gas Reduction




Pdf Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Global Warming




Carbon Footprint Scopes Practical Summary Green Element Blog




Global Warming Potential Definition And Examples




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Q Tbn And9gcqx8qqb7vyjubela12bb Jefr3jui9po9norhhsaq Qhlnrfuaa Usqp Cau




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Live Science




Carbon Dioxide Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



What Is The Relationship Between Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Socratic



Greenhouse Gas Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
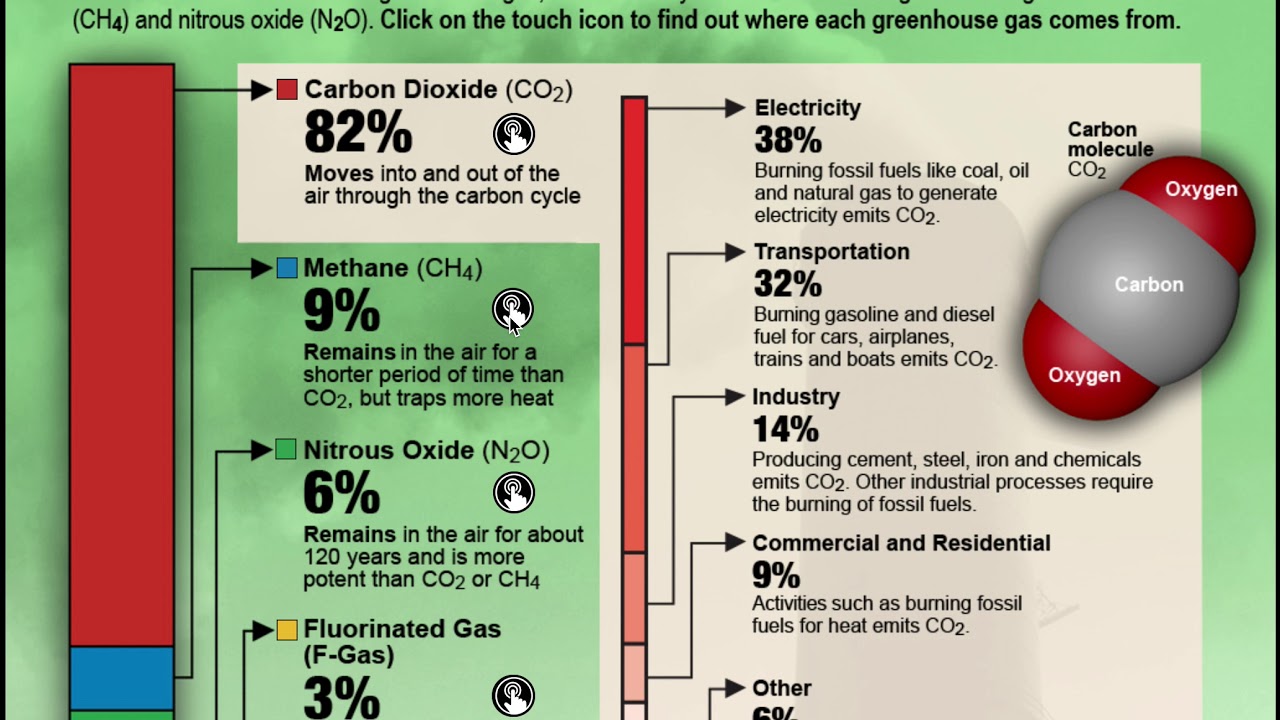



What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Green Chemistry What Is It Encourages Environmentally Conscious Behaviour Reduces And Prevents Pollution Reduces The Destruction Of The Planet Ppt Download




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



Natural Sources Of Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



Climate Change Comic Stripe Storyboard Von Ce26d5bb




Difference Between Complete Combustion And Incomplete Combustion Definition Properties Examples Exothermic Reaction Light Energy Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)



Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
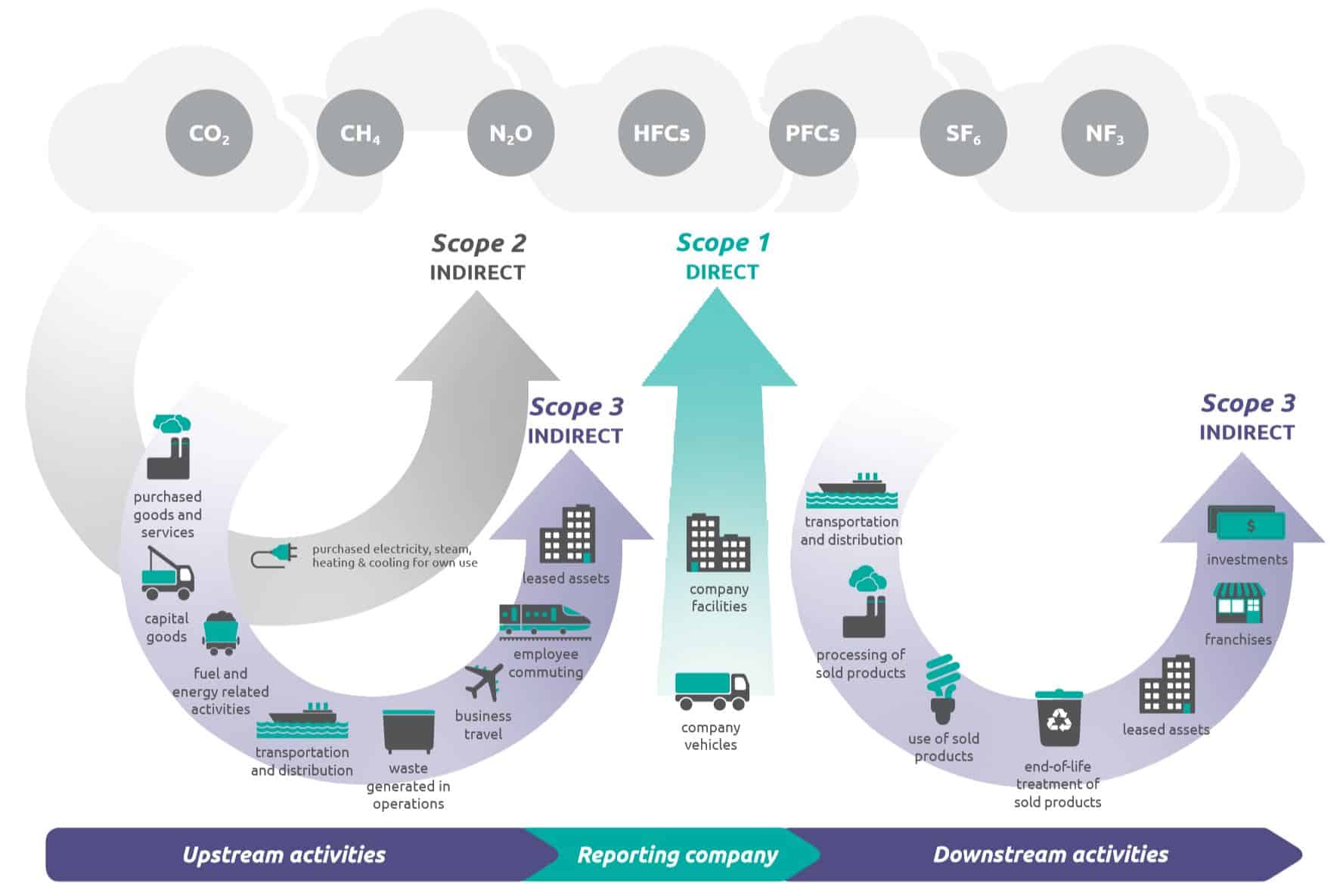



What Is The Difference Between Scope 1 2 And 3 Emissions Compare Your Footprint




Carbon Offsets Explained Reduce Emissions Climate Change



Untitled Document




Infographic What Is A Tonne Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Citizens For Public Justice




What Are Hydrofluorocarbons Eia Global



Meet The Greenhouse Gases Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



Umanitoba Ca Faculties Afs Discovery Centre Greenhousegas Media Grade 5 Pdf Pdf




What Is Climate Change Definition And Examples Market Business News




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect



Carbon Cycle And The Earth S Climate




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



1




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases And The Greenhouse Effect Kids Environment Kids Health National Institute Of Environmental Health Sciences




Greenhouse Gases Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Effect E 3 Pages Definitions 2 Description 3 Greenhouse Gases 4 Greenhouse Gases Effect On Atmosphere Ppt Download




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Q Tbn And9gcrevtfvebbghz5zkkbq1akjhfs4 Gwdrbwpqnmfiixo2oqlgyw8 Usqp Cau



The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Definition Impact Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science
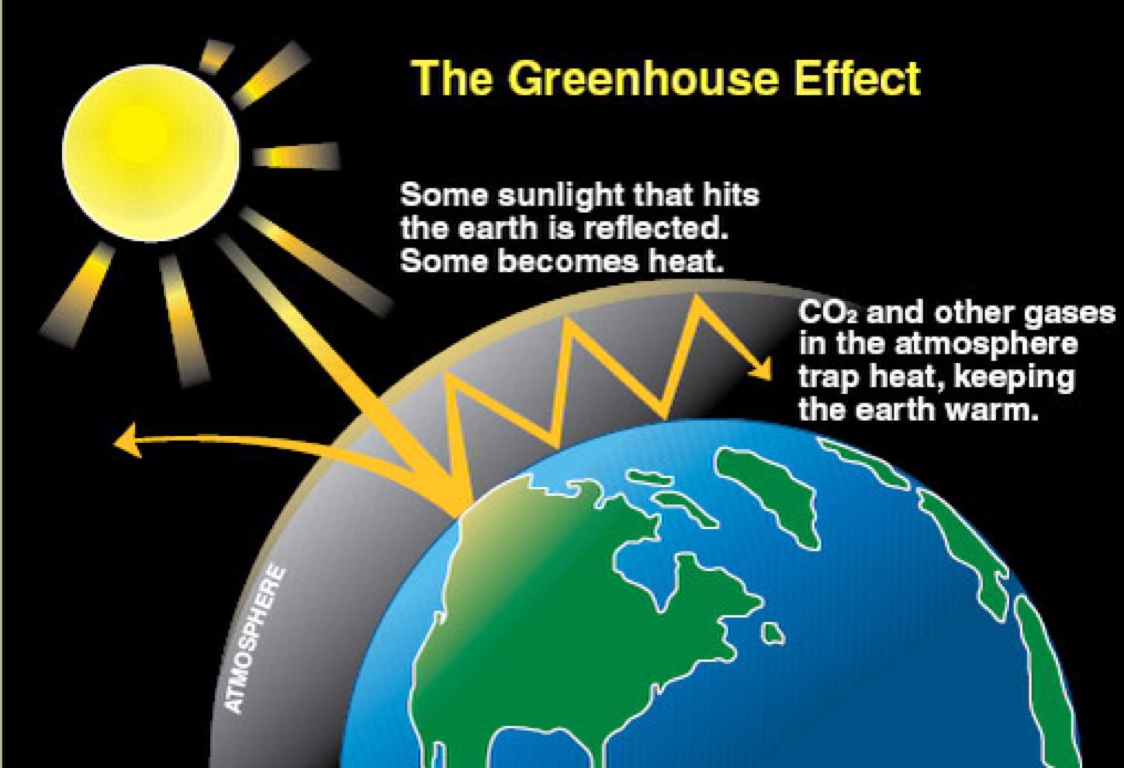



What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic




Iso 2 19 En Greenhouse Gases Part 2 Specification With Guidance At The Project Level For Quantification Monitoring And Reporting Of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions Or Removal Enhancements




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿